muscle fiber orientation
1 The pennation angle in unipennate muscles has been measured at a variety of. Muscle fiber orientation in the left ventricular myocardial layer was histometrically estimated in normal concentric and eccentric hypertrophied hearts.
Muscle Histology Flashcards Chegg Com
FO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce ATP but produce higher tension contractions than SO fibers.

. However the creation of fiber orientation maps for computational analyses remains. The metabolite profile changes due to the muscle fiber orientation demonstrate that the positioning potentially causes inaccuracy in 1 H-MRS spectrum analysis. Muscle fiber orientation curvature and length is known to change with changes in force within the muscle Herbert et al.
Tending to one point of focus. In the inner layer the inclination was. Muscle fiber directions along the muscles of the beef round have not been documented.
The proximal and distal musculotendinous junctions in muscles of the upper and lower extremities were identified. This fiber orientation provides a good compromise in providing for both range of motion and power for. Results showed that the fibres of obliquus externus abdominis were about 4more vertical than the lower edge of the eighth rib.
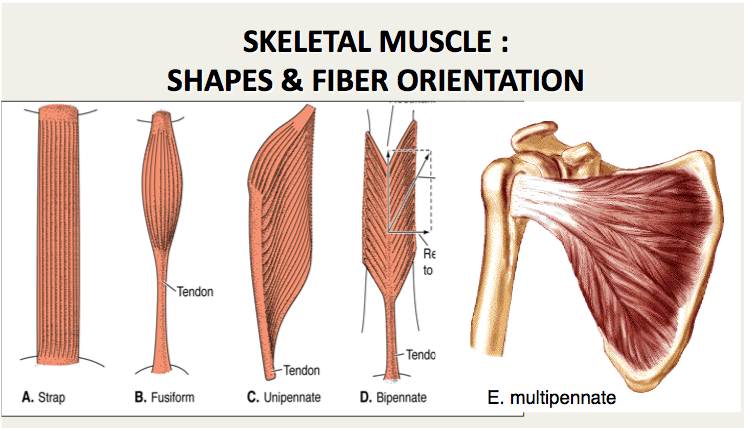
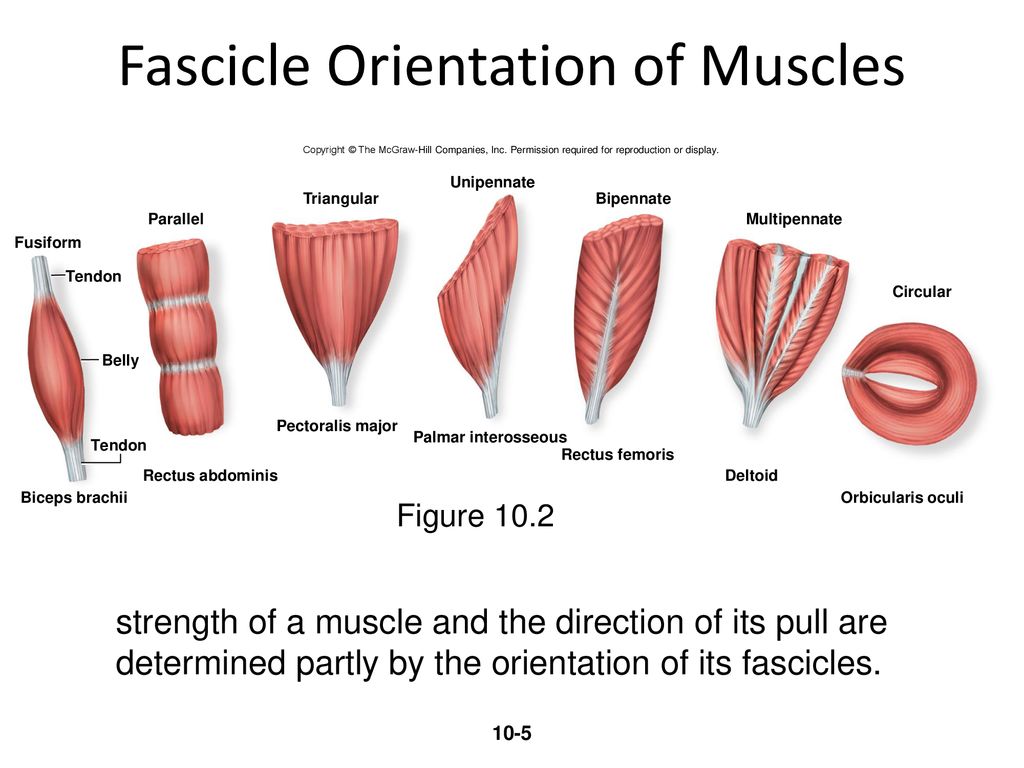
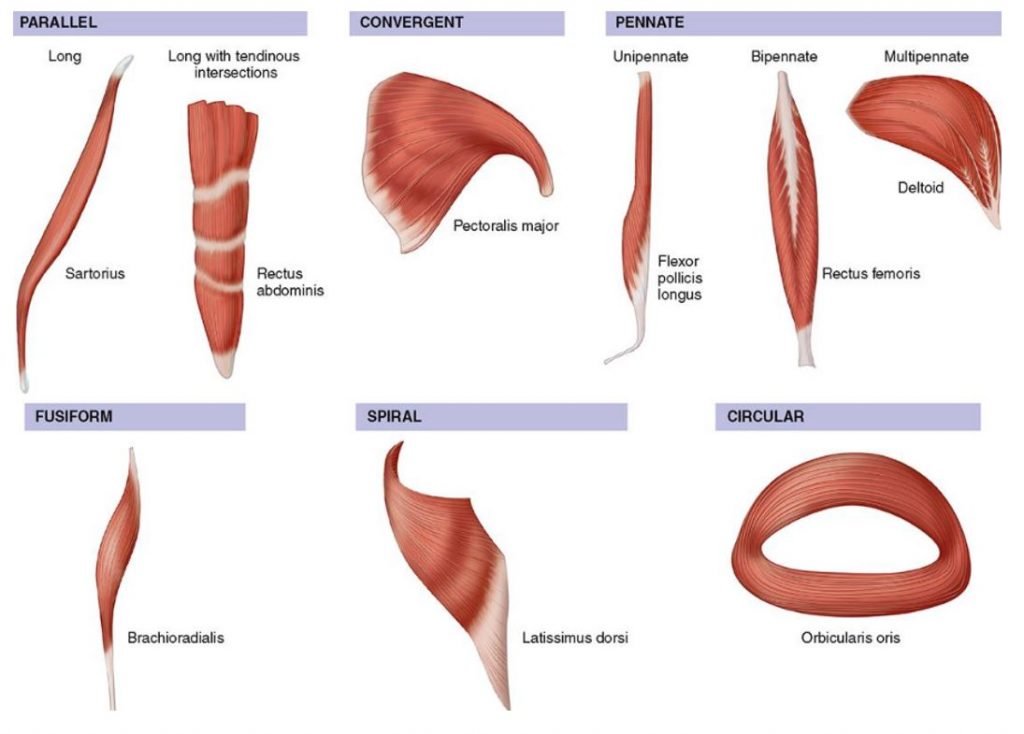
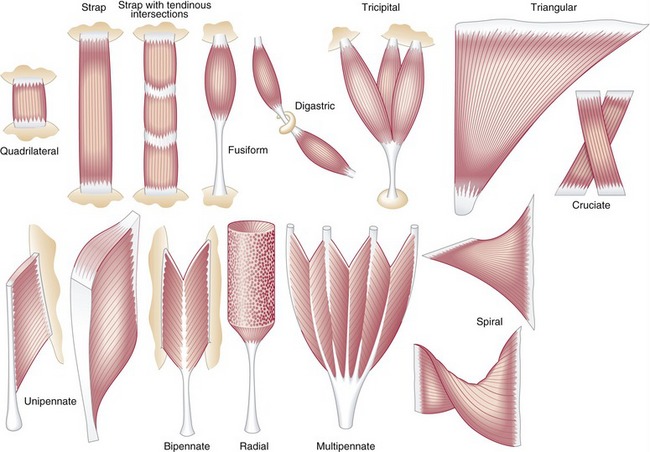
Analysis the orientation of muscle fibers in planarians - GitHub - walkernoreenmuscle_fiber_orientation. Thirty-seven embalmed cadavers 19 males and 18 females were examined. Muscle fiber orientation STUDY PLAY parallel strap have fibres which as the name suggests run parallel to each other.
Muscle fiber orientation in the left ventricular myocardial layer was histometrically estimated in normal concentric and eccentric hypertrophied hearts. The dense muscle fiber microstructure gives rise to orientation dependent mr features with anisotropic overall motion of the creatine cr and phosphocreatine pcr molecules causing residual dipolar couplings first described for the total observed creatine tcr crpcr resonances 1 2 while orientation dependence was later also reported for. The three types of muscle fiber are slow oxidative SO fast oxidative FO and fast glycolytic FG.
For optimal pick-up of electromyographic EMG signals surface electrodes are best aligned in parallel with the fibre orientation of the underlying muscle. The knowledge of muscle fiber direction is important during meat fabrication so that muscles can be cut across the grain to improve the tenderness. The angle of inclination of muscle fibers from coronal section was largest in the innermost and outermost zones and was progressively diminished toward the middle layer in all the hearts.
The angle of inclination of muscle fibers from coronal section was largest in the innermost and outermost zones and was progressively diminished toward the middle layer in all the hearts. This study aimed to measure muscle fibre orientation and other parameters of muscle morphology of the abdominal muscles in relation to palpable bony landmarks. Some textbooks include Fusiform muscles in the parallel group.
They are normally long muscles which cause large movements are not very strong but have good endurance. The ECM plays an essential role in the growth attachment alignment and differentiation of myoblasts and is part of the signaling mechanism involved in myogenesis. Orientation of muscle fibers was determined.
A skeletal muscle fiber arrangement in which the fibers are in an somewhat parallel orientation spread across a wide bone surface at the origin and coming together at a tendon attachment at the insertion. The figure here presents the six types. Differences in sarcomere alignment and length strongly affect a muscles force- and power-generating capacity.
This study aimed to measure muscle fibre orientation and other parameters of muscle morphology of the abdominal muscles in View on PubMed Save to Library Create Alert 310 Citations. Muscle Fiber Alignment. This study reveals that the muscle orientation at 0 30 60 and 90 to the main magnetic field significantly affects the metabolite profile and quantification.
SO fibers use aerobic metabolism to produce low power contractions over long periods and are slow to fatigue. Examples include Sartorius and Sternocleidomastoid. Muscle metabolite visibilities in MR spectroscopy and water T2 times depend substantially on muscle fiber orientation relative to B0.
Two groups of muscle fibers which are located within the deep perineal pouch and surround the urethra are called the urethral sphincter Oelrich 1980 The urethral sphincters are used to control the exit of urine in the urinary bladder through the urethra mainly the external urethral sphincter which is under voluntary control. Smoothly varying muscle fiber orientations in the heart are critical to its electrical and mechanical function. Measurements using common surface.
Charac-terization of all muscles in the beef round based on their intramuscular tenderness and muscle fiber orienta-. This study was designed to locate the middle of the muscle fibers of commonly injected muscles thus identifying the endplate zone of these muscles. Water T1s were similar between orientations but T2s were statistically significantly shorter by 1 ms in the parallel orientation P 0002.
Analysis the orientation of muscle fibers in planarians. Broadly there are two main approaches to extracting fiber orientationcurvature automatically from ultrasound. The muscle fibers in native skeletal muscle are closely packed together in an extracellular matrix ECM to form an organized tissue with high cell density and three-dimensional 3D cellular orientation.
Unipennate muscles are those where the muscle fibers are oriented at one fiber angle to the force-generating axis and are all on the same side of a tendon. In contrast magnetization transfer rates appear to depend on muscle composition rather than. Tending to approach each other.
From detailed histological studies and diffusion tensor imaging we now know that fiber orientations in humans vary gradually from approximately 70 in the outer wall to 80 in the inner wall. The long axis of a muscle determines the arrangement of individual fibers from an imaginary line drawn through the origin and insertion or the fiber angle relative to the force-generating axis.

Marginal M Posterior P And Anterior A Fibers In The Soleus Download Scientific Diagram

Pennate Muscle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Five Possible Fiber Orientations In Intact Whole Muscle A Fusiform Download Scientific Diagram

3 Orientation Of Cardiac Muscle Fibers Download Scientific Diagram

11 2 Explain The Organization Of Muscle Fascicles And Their Role In Generating Force Anatomy Physiology
Ppt 4 Muscle Unit Chapter 10 1 Intro To Naming And Identifying Muscles Of The Human Body Ppt Download

Skeletal Muscle Shapes Fusiform Muscles Thick In Middle And Tapered At Ends Parallel Muscles Have Parallel Muscle Fibers Convergent Muscle Broad At Ppt Download

Fdi Muscle Fiber Tracks Derived From The Dwi Data In Three States At Download Scientific Diagram

Pennate Muscle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Classification Of Muscles Based On The Directions Of Muscle Fibers The Download Scientific Diagram
How Muscles Work Part 2 Of 2 Shapelog

Myocardial Fiber Orientation And Direction Of Rotation Myocardial Download Scientific Diagram

Fdi Muscle Fiber Tracks Derived From The Dwi Data In Three States At Download Scientific Diagram
Muscle The Primary Stabilizer And Mover Of The Skeletal System Clinical Gate

A Unilateral Longitudinal Muscle Contraction Red Arrows Indicate Download Scientific Diagram

Myocardial Mechanics Structure And Function Of Myocardial Fibers Ecg Echo
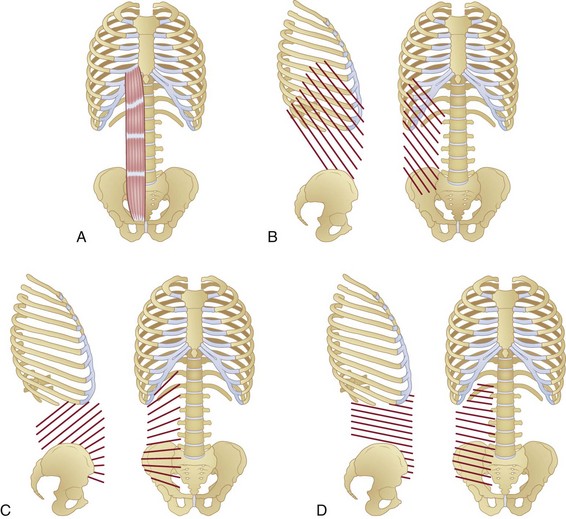
Anatomy And Mechanics Of The Abdominal Muscles Musculoskeletal Key
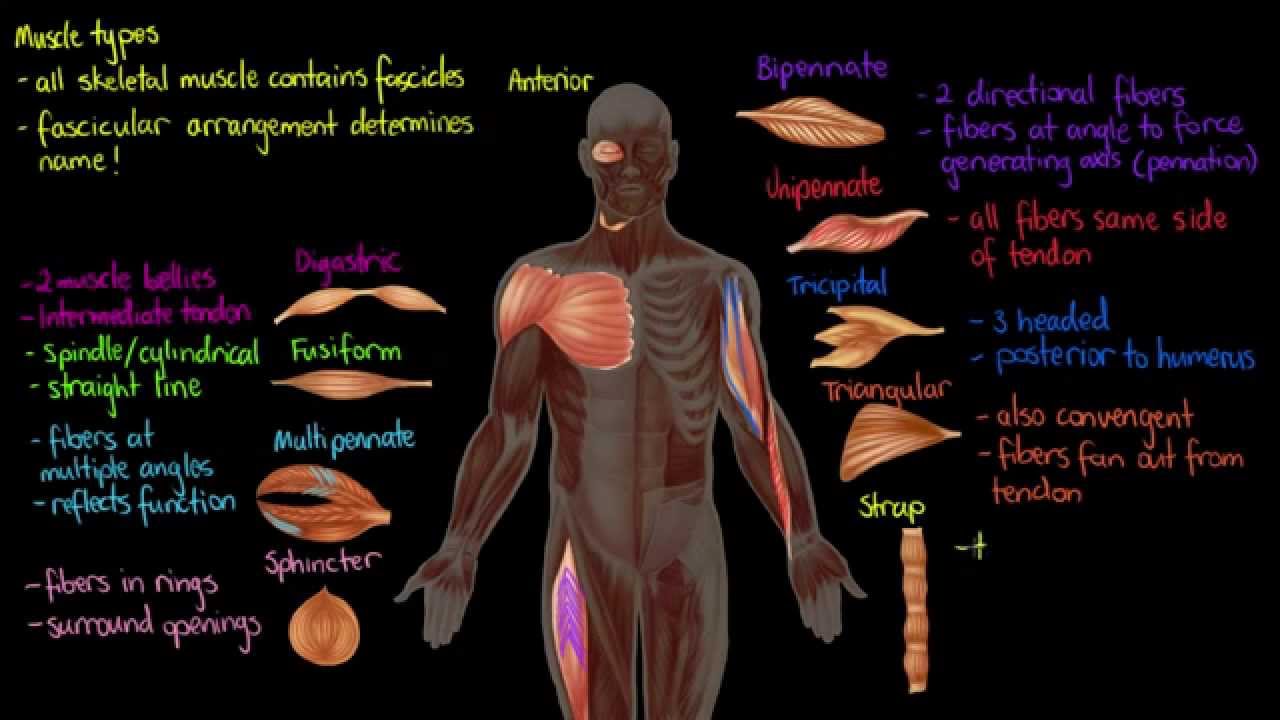
Comments
Post a Comment